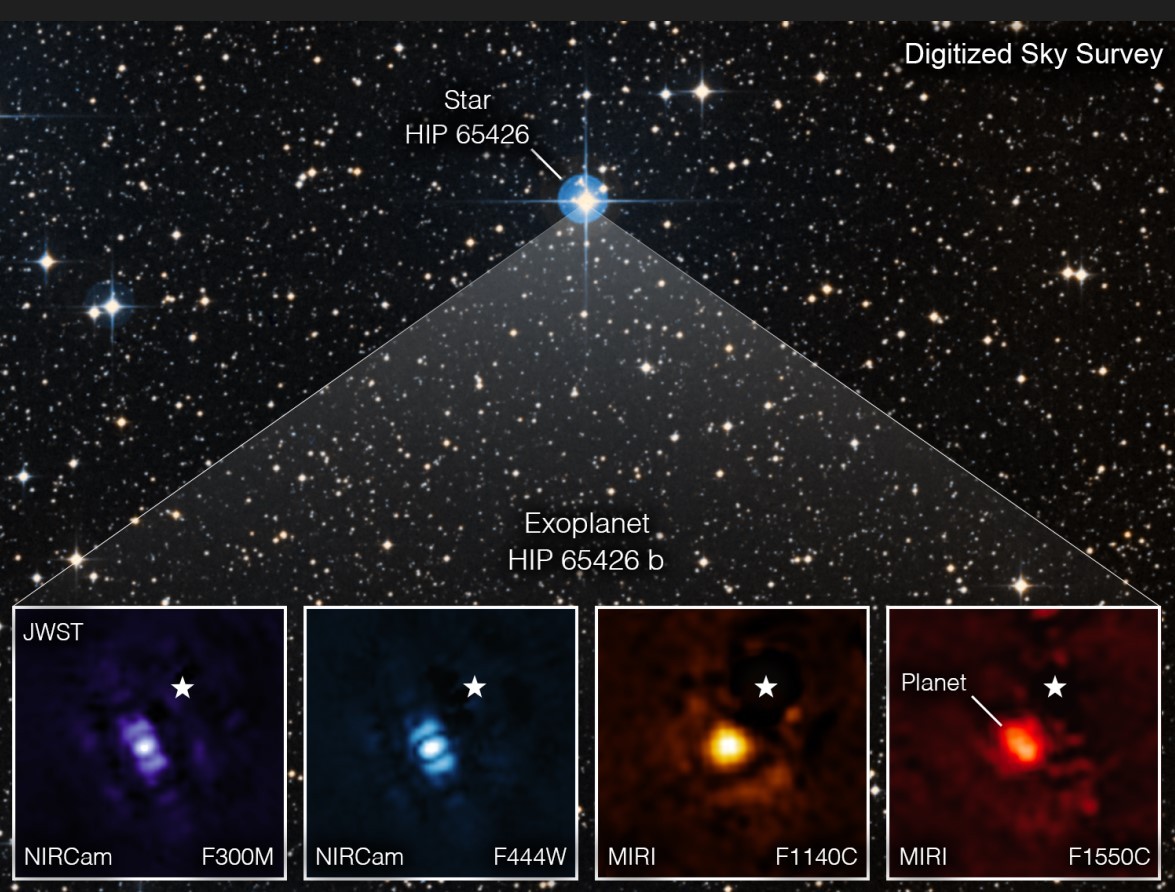
Astronomers have captured a direct image of a planet outside of our solar system for the first time using NASA’s Webb Space Telescope. Since the exoplanet is a gas giant and lacks a stony surface, life cannot exist there.
The image captured by James Webb Space Telescope, as seen through four different light filters, demonstrates how Webb’s strong infrared vision can readily capture worlds outside of our solar system, opening the door to follow-up observations that will provide more information than ever before about exoplanets.
“This is a transformative moment, not only for NASA Webb but also for astronomy generally,” said Sasha Hinkley, associate professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Exeter in the United Kingdom, who led these observations with a large international collaboration. Webb is an international mission led by NASA in collaboration with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
NASA’s Webb captures the direct images of the mysterious exoplanets
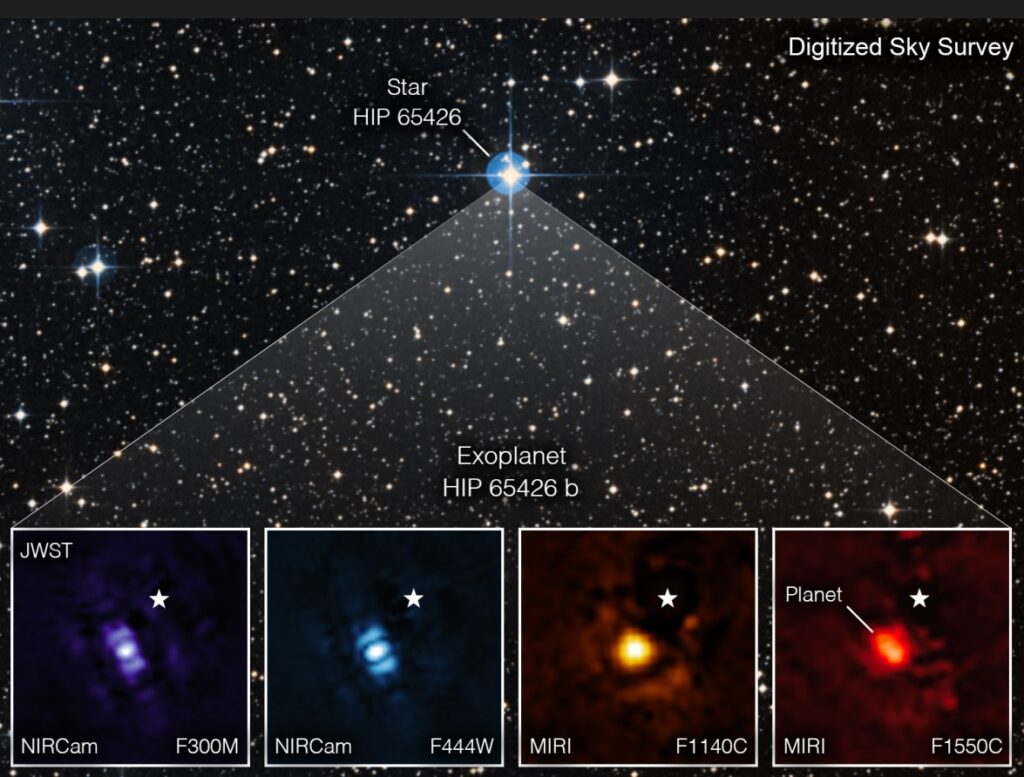
This image shows the exoplanet HIP 65426 b in different bands of infrared light, as seen from the James Webb Space Telescope: purple shows the NIRCam instrument’s view at 3.00 micrometers, blue shows the NIRCam instrument’s view at 4.44 micrometers, yellow shows the MIRI instrument’s view at 11.4 micrometers, and red shows the MIRI instrument’s view at 15.5 micrometers.
These images look different because of the ways the different Webb instruments capture light. A set of masks within each instrument, called a coronagraph, blocks out the host star’s light so that the planet can be seen.
The small white star in each image marks the location of the host star HIP 65426, which has been subtracted using the coronagraphs and image processing. The bar shapes in the NIRCam images are artifacts of the telescope’s optics, not objects in the scene. (Unlabeled version.) Credit: NASA/ESA/CSA, A Carter (UCSC), the ERS 1386 team, and A. Pagan (STScI).
The exoplanet in Webb’s image, called HIP 65426 b, is about six to 12 times the mass of Jupiter, and these observations could help narrow that down even further. It is young as planets go — about 15 to 20 million years old, compared to our 4.5-billion-year-old Earth.
Astronomers discovered the planet in 2017 using the SPHERE instrument on the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile and took images of it using short infrared wavelengths of light. Webb’s view, at longer infrared wavelengths, reveals new details that ground-based telescopes would not be able to detect because of the intrinsic infrared glow of Earth’s atmosphere.
Researchers have been analyzing the data from these observations and are preparing a paper they will submit to journals for peer review. But Webb’s first capture of an exoplanet already hints at future possibilities for studying distant worlds.
Since HIP 65426 b is about 100 times farther from its host star than Earth is from the Sun, it is sufficiently distant from the star that Webb can easily separate the planet from the star in the image.